PDT/PDD research
What is PDD
Photodynamic Diagnosis
PDD is a method of diagnosing the presence of cancer tissues by
using the properties of photosensitive materials to be optically
fluorescent in certain cancer cells by light sources with constant wavelengths.
What is PDD?
Photodynamic diagnosis (PDD) is a method of diagnosing the presence of cancer tissues by using the properties of photosensitive materials to be optically fluorescent in certain cancer cells by light sources with constant wavelengths. In the beginning, a method to locate bladder cancer was attempted with an endoscope using fluorescent light after administering photosensitive materials through blood vessels, but clinical applications were limited due to photosensitive reactions and other restrictive factors. However, a new diagnostic method has recently been developed to diagnose bladder cancer through a specially designed fluorescence endoscope after local injection of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), known as precursor to the endogenous phosphorpyrin IX (PIX). (Korean Society of Urinary Sciences, 1999 Vol. 40, No. 7, 886-890).
- Early cancer diagnosis by PDD for ALA can dramatically increase the rate of early detection of cancer patients by examining early cancer or dysplastic cancer (pre-cancer before cancer) through PDD, which could not be examined by conventional diagnostic methods. PDD can check for all early and dysplastic cancers, including lung, stomach, bladder, uterus, and throat, which can be identified by endoscopy, especially for regular examinations for recurrence after cancer surgery. It also serves as a guide for surgery such as brain tumors, bladder cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer, which show clear boundaries between cancer and normal cells. Due to these needs, Germany's KARL STORZ GmbH supplies fluorescent endoscopes for PDD worldwide. The 5-ALA, a phosphor-sensitive drug used in PDD, is the world's most popular with ALA conferences and regular ALA symposiums in the U.S. and Japan, and is rapidly expanding into the field of PDT procedures.
PDD/PDT Status
Traditional cancer treatments, such as surgical surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, are extremely limited, and cause serious side effects by damaging normal tissue, so a new anti-cancer treatment (Tumor-Specific Therapy) that preserves the function of normal tissue and treats tumors only, is being developed. Thus, leading biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies worldwide are scrambling to develop anti-cancer drugs based on these new treatments. Among them, wide-area dynamic treatment technology (PDT/PDD) is the most advanced clinical technology that is currently experiencing the most widespread increase in application compared to other treatment methods being developed or clinical trials since 1976. PDT is a new medical technology that meets unmet medical needs, and in the United States, it was approved as an esophageal cancer treatment in 1995 and expanded to an early lung cancer treatment in 1998. Japan approved the medical treatment of PDT in 1994, while Germany and Europe have been doing PDT treatment since 1996.
Chart
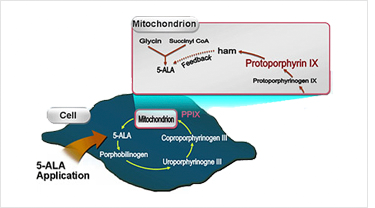
5-ALA
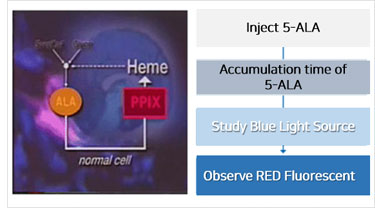
5-ALA from 5DD
Transferring Drugs
| For Drinking | For Inhaling | For Injecting |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

